Keeping your WordPress application up-to-date with the latest version is an important step in maintaining a secure site. If you find the update process difficult or simply forget to keep track of the new releases, our automatic WordPress software and plugin updates are for you. With WordPress, writing, editing, and publishing content to your site is as easy as 1, 2, 3. To get started, click on the “Posts” tab in the left side menu area, then click on “Add New”. To add images to your content, all you need to do is click on the “Add Media” button found right below the Title field. Get Hosting and Install WordPress (note - I’ll earn a small commission and you’ll earn a discount when you use this link): https://createaprowebsite.com/host. Installing WordPress is a very easy process with their simple to use user interface. Before you follow the next steps, make sure you are logged in to your Bluehost account. Log in to your Bluehost cPanel account. Find the Website section and select “Install WordPress”.
Getting Started Resource Center / 10-Minute Tutorials / ..
Amazon Lightsail is the easiest way to get started with AWS. It offers virtual servers, storage, databases and networking, plus a cost-effective, monthly plan.
This tutorial shows you how to launch and configure a WordPress instance on Lightsail. It includes steps to connect to your instance by using SSH, sign in to your WordPress website, create a static IP and attach it to your instance, create a DNS zone, and map it to your instance.
When you're done with this tutorial, you will have the fundamentals to get your WordPress website up and running in Amazon Lightsail.
| About this Tutorial | |
|---|---|
| Time | 10 minutes |
| Cost | Free Tier Eligible |
| Use Case | Compute |
| Products | Amazon Lightsail |
| Audience | Developer |
| Level | Beginner |
| Last Updated | March 23, 2020 |
Already have an account? Sign-in
Complete the following steps to get your WordPress instance up and running on Lightsail.
Note: For more information about creating an instance in Lightsail, see Creating an Amazon Lightsail instance in the Lightsail documentation.
- Choose Linux/Unix as the platform.
- Choose WordPress as the blueprint.
- Must be unique within each AWS Region in your Lightsail account.
- Must contain 2 to 255 characters.
- Must start and end with an alphanumeric character or number.
- Can include alphanumeric characters, numbers, periods, dashes, and underscores.
3. Connect to your instance via SSH and get the password for your WordPress website
The default password to sign in to the administration dashboard of your WordPress website is stored on the instance.
Complete the following steps to connect to your instance using the browser-based SSH client in the Lightsail console, and get the password for the administration dashboard.
Note: For more information, see Getting the application user name and password for your Certified by Bitnami' instance in Amazon Lightsail.
4. Sign in to the administration dashboard of your WordPress website
Now that you have the password for the administration dashboard of your WordPress website, you can sign in. In the administration dashboard, you can change your user password, install plugins, change the theme of your website, and more.
Complete the following steps to sign in to the administration dashboard of your WordPress website.
Note: For more information, see Getting the application user name and password for your Certified by Bitnami' instance in Amazon Lightsail.
In the address, replace PublicIpAddress with the public IP address of your WordPress instance. You can get your instance's public IP address from the Lightsail console as shown in the following image:
b. Log into your instance.
- In the Username or Email Address box, enter 'user'.
- Password box, enter the default password obtained earlier in this tutorial.
- Choose Log in.
You are now signed in to the administration dashboard of your WordPress website where you can perform administrative actions. For more information about administering your WordPress website, see the WordPress Codex in the WordPress documentation.
5. Create a Lightsail static IP address and attach it to your WordPress instance
The default public IP for your WordPress instance changes if you stop and start your instance. A static IP address, attached to an instance, stays the same even if you stop and start your instance.
Wordpress Blogs Free
Complete the following steps to create a static IP address and attach it to your WordPress instance.
Note: For more information, see Create a static IP and attach it to an instance in Amazon Lightsail.
b. Choose the Networking tab, then choose Create static IP.
c. The static IP location, and attached instance are pre-selected based on the instance that you chose earlier in this tutorial.
6. Create a Lightsail DNS zone and map a domain to your WordPress instance
Transfer management of your domain's DNS records to Lightsail. This allows you to more easily map a domain to your WordPress instance, and manage more of your website’s resources using the Lightsail console.
New torrent software. Complete the following steps to create a Lightsail DNS zone and map a domain to your WordPress instance.
Note: For more information, see Creating a DNS zone to manage your domain’s DNS records in Amazon Lightsail.
a. On the Networking tab of the Lightsail home page, choose Create DNS zone.
b. Enter your domain, then choose Create DNS zone.
c. Make note of the name server address listed on the page.
You add these name server addresses to your domain name’s registrar to transfer management of your domain’s DNS records to Lightsail.
You have used Amazon Lightsail to launch and deploy a WordPress instance.
Amazon Lightsail is a great choice to develop, build, and deploy a variety of applications like WordPress, websites, and blog platforms.
Was this tutorial helpful?
Recommended next steps
Create a snapshot
Creating a snapshot of your Linux or Unix instance in Amazon Lightsail.
Enable or disable snapshots
Enabling or disabling automatic snapshots for instances or disks in Amazon Lightsail.
Add storage
Creating and attaching additional block storage disks to your Linux-based Lightsail instances
Need Help Getting Started with WordPress?
Start a BlogStep by step guide on how to start a blog.Make a Website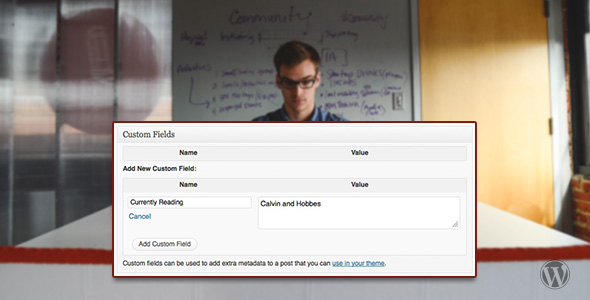 Beginners guide on how to make a website.EcommerceCompare the best eCommerce plugins.FormsCompare the best form builder plugins.MembershipCompare the best membership plugins.SecurityCompare the best security plugins.PerformanceCompare the best caching plugins.
Beginners guide on how to make a website.EcommerceCompare the best eCommerce plugins.FormsCompare the best form builder plugins.MembershipCompare the best membership plugins.SecurityCompare the best security plugins.PerformanceCompare the best caching plugins.Using Wordpress For Business Website
AnalyticsCompare the best analytics plugin.Lead GenerationCompare the best lead generation plugins.Email MarketingCompare the best email marketing services.BackupsCompare the best backup plugins.SEOCompare the best SEO plugins and tools.GalleryCompare the best gallery plugins.Social MediaCompare the best social media plugins.Page BuildersCompare the best page builder plugins.BookingCompare the best booking plugins.LMSCompare the best LMS plugins for WordPress.TranslationCompare the best translation plugins.AffiliateCompare the best affiliate plugins.Live ChatCompare the best live chat plugins.Business PhoneCompare the best business phone services.CRMCompare the best CRM software. SMTPCompare the best SMTP services.Website BuilderCompare the best website builders.Blogging PlatformCompare the best blogging platforms.
SMTPCompare the best SMTP services.Website BuilderCompare the best website builders.Blogging PlatformCompare the best blogging platforms.The Ultimate WordPress Launch Checklist
Latest from our Blog
What Is DDoS Attack and How To Prevent It? 5 Easy Steps
Using Wordpress
7 Best Cloud Storage Apps for Businesses [Free Included]
How Effective Are Bluehost SEO Tools? (Review 2021)
5 Best Client Management Software for Small Businesses
See All Articles »The Ultimate WordPress Launch Checklist
